虚拟滚动列表组件
为什么需要开发这样一个组件
- 可视化大屏需要这样的列表展示组件
- 虚拟滚动的需求是逐渐演变的,初期只需要列表展示的组件,一次性展示所有数据,数据量大的时候导致页面渲染卡顿
解决方案
- 分页加载,每页控制展示条目,性能可控,但是大屏展示一般不需要操作,分页的方案不可取
- 无限滚动,初始加载一小部分,越滚动加载越多,性能问题是迟早的事
- 虚拟滚动
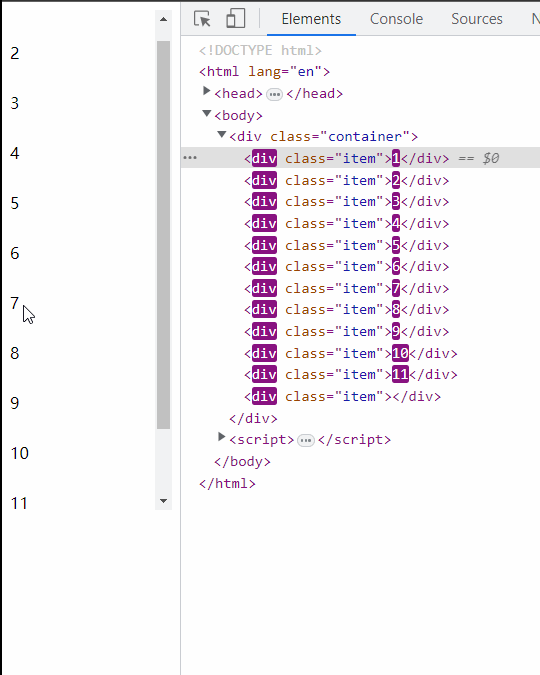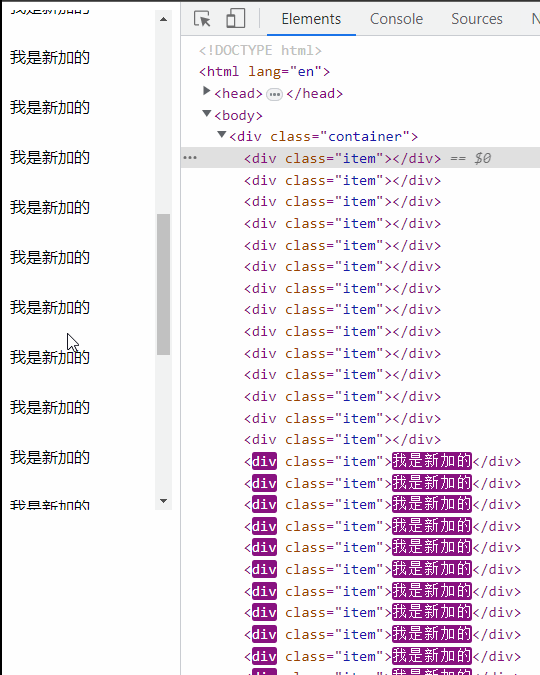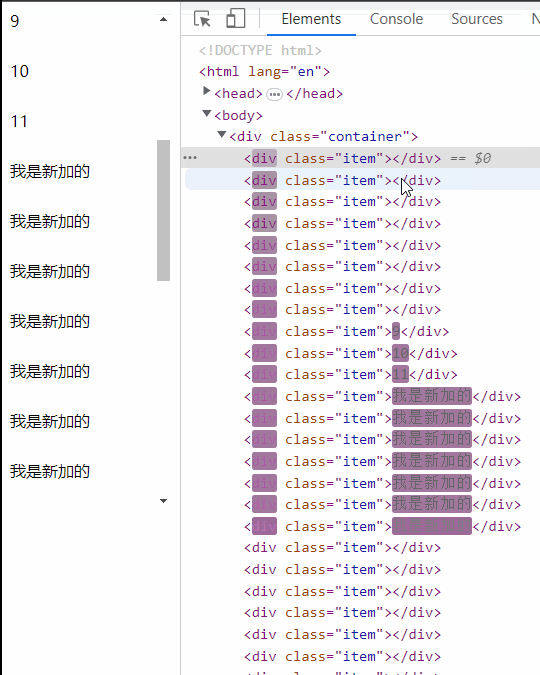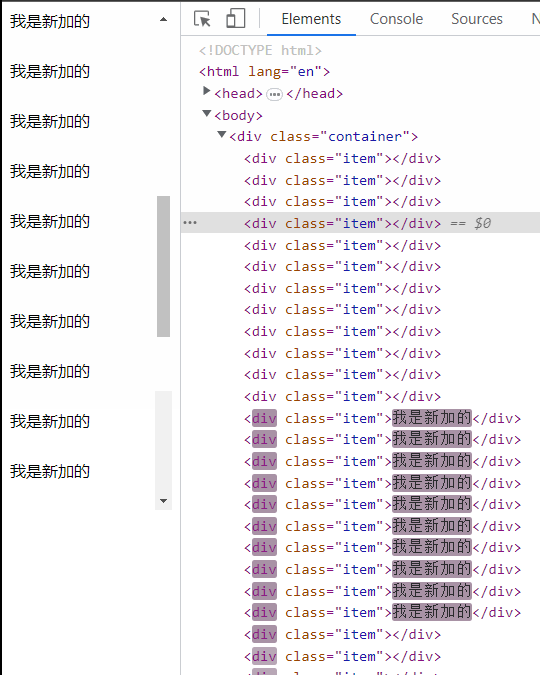
懒加载,无限滚动
优点:实现相对简单,不需要额外引入类库。不用考虑每一个 item 的高度有多少。
缺点:
- 频繁下拉导致数据量越来越多,滚动条越来越短
- 已经加载过的滚动隐藏区域数据没有做渲染上处理
- 页面切换回来之后列表的滚动状态丢失,需要重新滚动
具体实现:
首先两个概念:
- Element.scrollHeight 这个只读属性是一个元素内容高度的度量,包括由于溢出导致的视图中不可见内容。
- Element.scrollTop 属性可以获取或设置一个元素的内容垂直滚动的像素数。 scrollHeight 内容区域的全部高度(包含隐藏起来的)- scrollTop 已经卷起来的高度 = 剩余的内容高度(可视区域高度 + 还没卷起来的高度) 判断这个剩余的内容高度 和 设定的外层容器(可视区域)的高度,如果小的,说明滚动内容结束了,就需要展示新增的数据。
html
<style>
.container {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
overflow: auto;
}
.item {
height: 50px;
}
</style>
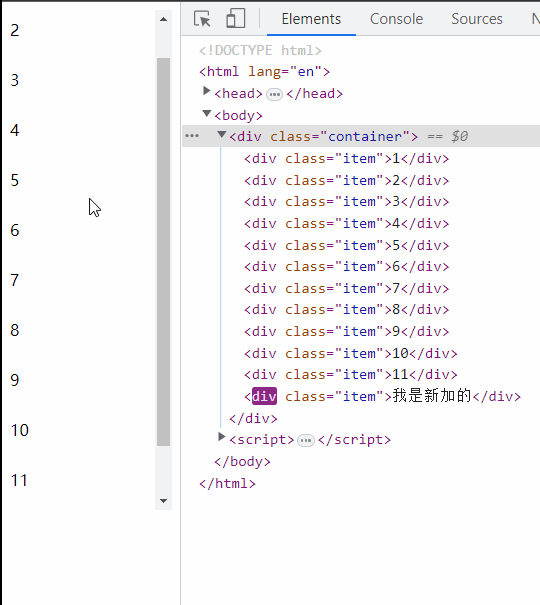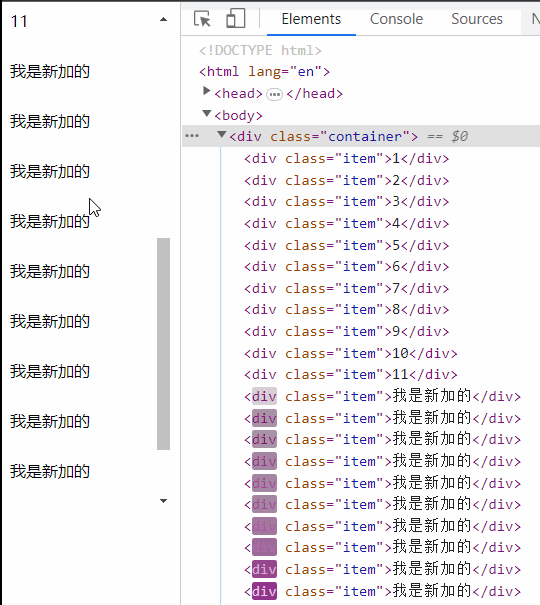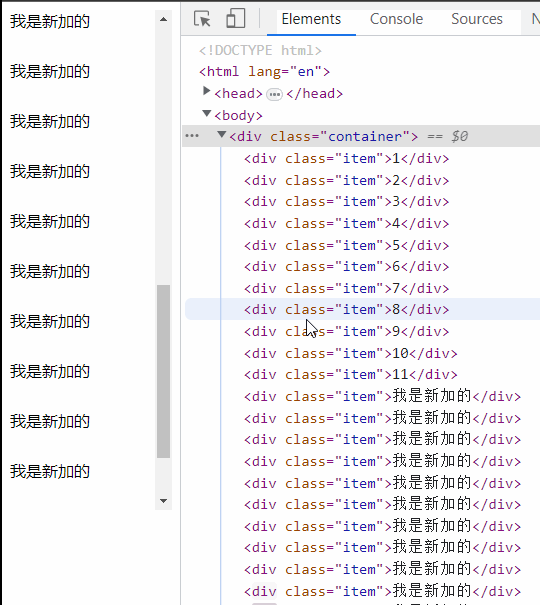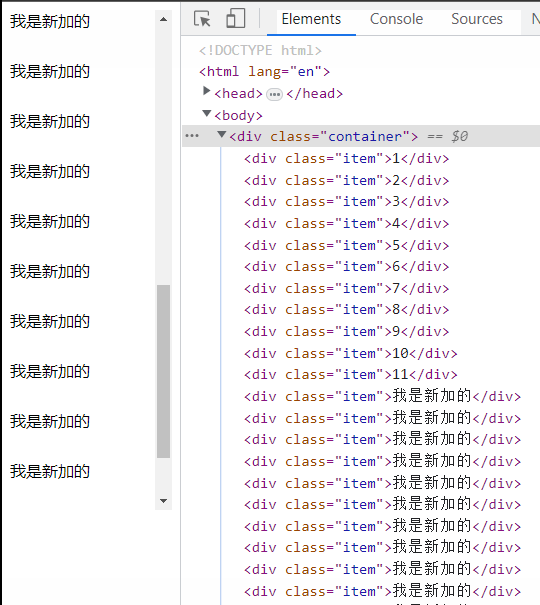
<div class="container">
<div class="item">1</div>
<div class="item">2</div>
<div class="item">3</div>
<div class="item">4</div>
<div class="item">5</div>
<div class="item">6</div>
<div class="item">7</div>
<div class="item">8</div>
<div class="item">9</div>
<div class="item">10</div>
<div class="item">11</div>
</div>
<script>
const container = document.querySelector(".container");
container.addEventListener("scroll", () => {
const offset = container.scrollHeight - container.scrollTop;
const delta = 50;
if (offset <= 500 + delta) {
const newItemDom = document.createElement("div");
newItemDom.setAttribute("class", "item");
newItemDom.innerHTML = "我是新加的";
container.appendChild(newItemDom);
}
});
</script>
IntersectionObserver + 空div占位
js
container.addEventListener("scroll", () => {
// 如上...
observer();
});
function observer() {
const items = Array.from(container.children) || [];
console.log(items.length);
items.forEach((item) => {
const intersectionObserver = new IntersectionObserver(
function (entries) {
if (!entries[0].isVisible) {
entries[0].target.backup = entries[0].target.innerHTML || entries[0].target.backup;
entries[0].target.innerHTML = "";
return;
}
entries[0].target.innerHTML = entries[0].target.backup || entries[0].target.innerHTML;
},
{
threshold: [0, 1],
trackVisibility: true,
delay: 100,
}
);
intersectionObserver.observe(item);
});
虚拟列表
虚拟列表就是按需显示的一种显示,只对可视区域进行渲染,对非可见区域的数据不渲染或部分渲染的技术,从而提升性能 屏幕的可视区域高度200px , 列表项目的高度20px, 在屏幕中只能看到10个列表项,在首次渲染时候只需要加载10条数据 实现 动态计算获得可视区域的列表项,将不可视区域内存在的列表项删除
- 当前可视区域起始数据索引 startIndex
- 计算当前可视区域结束数据索引 endIndex
- 计算当前可视区域的数据,渲染到页面上
- 计算 startIndex对应的数据在整个列表中的偏移位置 startOffset并设置到列表上
html
<style>
.container {
height: 500px;
overflow: auto;
}
.item {
height: 40px;
}
</style>
<div class="container"></div>
<script>
const data = [
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30,
];
const container = document.querySelector(".container");
window.onload = function () {
addList(data, container);
};
function addList(data, container) {
data.forEach((item) => {
const dom = document.createElement("div");
dom.setAttribute("class", "item");
dom.innerHTML = item;
container.appendChild(dom);
});
}
container.addEventListener("scroll", () => {
const scrollTop = container.scrollTop;
// 上边空白的高度
const topHeight = scrollTop;
const startIndex = Math.max(Math.ceil(topHeight / 40) - 2, 0);
const endIndex = startIndex + Math.ceil(500 / 40);
const show = data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1);
// 计算下边剩余的隐藏区域高度
const dataHeight = data.length * 40;
const bottomHeight = dataHeight - 500 - scrollTop;
const topDom = document.createElement("div");
const bottomDom = document.createElement("div");
topDom.style.height = topHeight + "px";
bottomDom.style.height = bottomHeight + "px";
// 还没到底
if (bottomHeight > -100) {
// 清空
container.innerHTML = "";
container.appendChild(topDom);
addList(show, container);
container.appendChild(bottomDom);
}
});
</script>
在vue3中实现
html
<template>
<div ref="container" class="box-border w-full h-full overflow-y-auto" @scroll="handleScroll">
<div ref="panel" :style="{ paddingTop: `${paddingTop}px` }">
<div
class="h-10 leading-10 text-[14px] text-[#979797] hover:text-[#59c7f9] hover:cursor-pointer flex"
v-for="item in visibleList"
:key="item.id"
>
<slot :row="item"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import type { PropType } from 'vue';
import type { ILiveTimeCompModel } from '@/types/menus';
const props = defineProps({
list: { type: Array as PropType<ILiveTimeCompModel[]>, default: () => [] }, // original list
showNum: { type: Number, default: 10 } // render items num
});
const { list, showNum } = toRefs(props);
const container = ref<HTMLElement>();
const panel = ref<HTMLElement>();
const itemHeight = 40;
let count = ref(showNum.value);
let startIdx = ref(0);
let endIdx = ref(showNum.value);
function initVisibleData() {
const containerHeight = container.value?.getBoundingClientRect().height || 300;
count.value = Math.ceil(containerHeight / itemHeight);
endIdx.value = Math.ceil(containerHeight / itemHeight);
}
onMounted(() => initVisibleData());
let visibleList = computed(() => list.value.slice(startIdx.value, endIdx.value));
let paddingTop = ref(0);
let panelHeight = ref(list.value.length * itemHeight);
function getPanelHeight() {
if (panel.value) panel.value.style.height = `${panelHeight.value}px`;
}
watch(
() => props.list,
(list) => {
panelHeight.value = list.length * itemHeight;
getPanelHeight();
},
{ deep: true }
);
onMounted(() => getPanelHeight());
function handleScroll(e: any) {
startIdx.value = Math.floor(e.target.scrollTop / itemHeight);
endIdx.value = startIdx.value + count.value;
paddingTop.value = startIdx.value * itemHeight;
}
</script>
使用案例
在 virtual designer 项目中实际使用